Photo: Theo Wargo/Getty Images for Firefly Music Festival

feature
A Guide To Southern Hip-Hop: Definitive Releases, Artists & Subgenres From The Dirty South
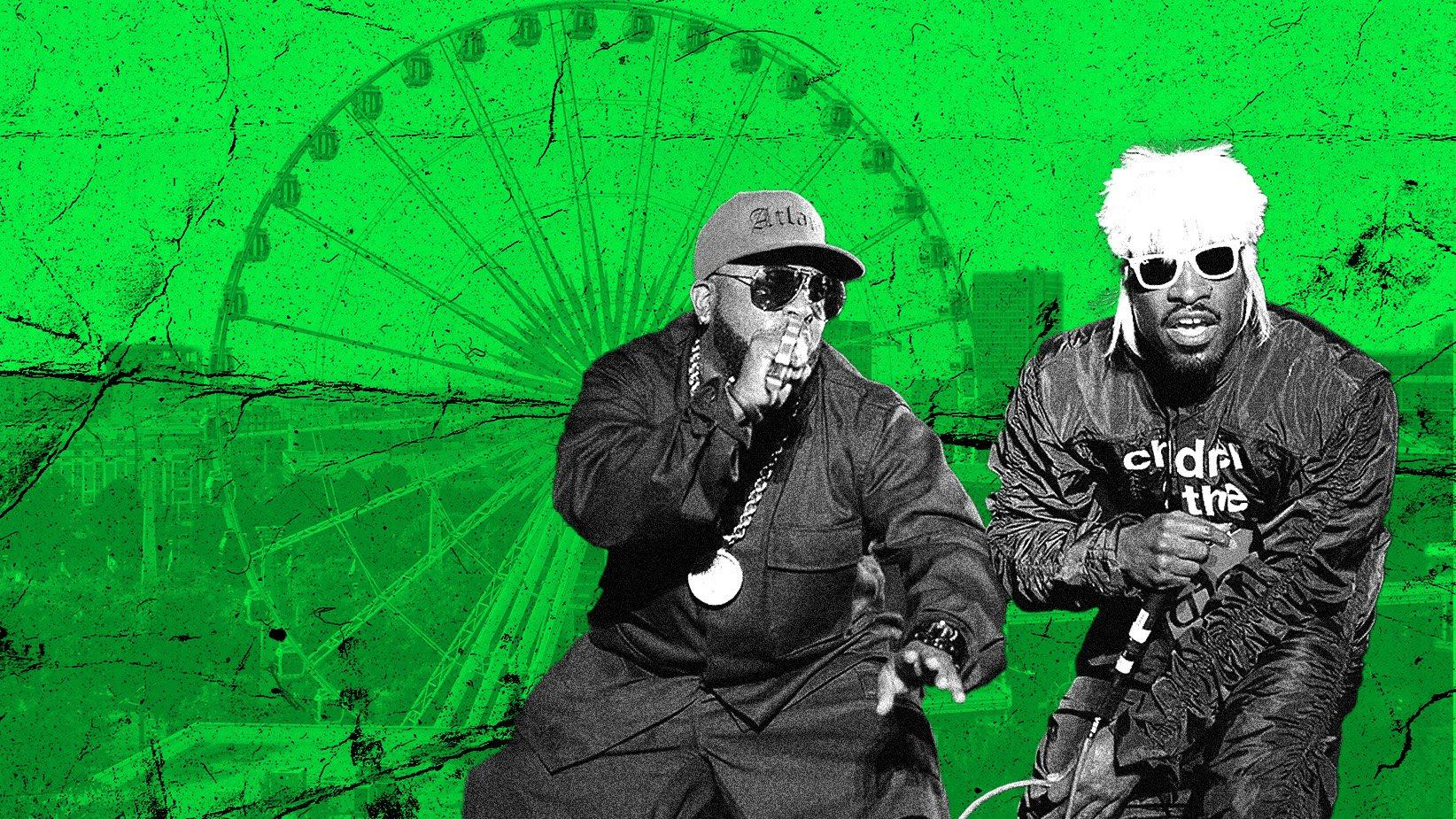
A geographical region far larger than the coasts, the South stretches from Texas to Virginia and includes myriad subgenres. Home to Outkast, Big Freedia, Ludacris and many others, the Third Coast has something to say in its own language.
For decades, hip-hop was regulated to New York, even though its musical stylings traveled to neighboring cities such as Boston and Philadelphia. In those cities, hip-hop was a cultural production of the city’s individual sound and history, rather than that of an entire region.
The power of L.A.'s emergent style of gangsta rap was the first attempt by an outsider to change hip-hop. As L.A. rappers began to give those from NYC rappers a challenge, the surrounding cities were solidified under the East Coast banner.
Often lost in the retelling of hip-hop’s birth are cities, regions and states in between the coasts. This absence may be due to the concentration of record labels and media corporations on the East and West Coast, or ill-informed beliefs that classify sections of the nation as backwards.
But expressions of hip-hop are expansive, and its culture is well represented in the South. A geographical region far larger than the coasts, the South stretches from Texas to Virginia. Along state lines, hip-hop finds itself at the intersection of Southernness and Blackness, leading to the creation of myriad subgenres.
Hip-hop sound traveled to New Orleans, where bounce was born in the city’s housing projects, and to Memphis where it became buck and crunk. In Atlanta, snap and trap music reign supreme, while electronic bass booms along the beaches of Miami. In every state, hip-hop took on a new voice, new moniker, and new identity.
With each innovation, the sound was able to expand beyond state lines to a diverse, wide ranging language along the region. Instead of accommodating the voices of the East or the West, the South a.k.a. the Third Coast entered into hip-hop with something to say in its own language.
Listen to the Spotify playlist below or visit Amazon Music, Pandora and Apple Music and take a journey through the diverse sounds of Southern hip-hop.
A Brief History Of Dirty South Hip-Hop
The birth of Southern hip-hop begins at the 1995 Source Awards, where Atlanta based hip-hop duo OutKast won Best New Artist and Best New Rap of the Year for their debut album, Southernplayalisticadillacmuzik. As André 3000 and Big Boi walked on stage, they were put with a chorus of boos. Although the ceremony was held at the height of East vs. West Coast rivalry, the coasts agreed on a singular purpose: The South had no claim to hip-hop.
There’s one thing the coasts don’t know about Southerns, especially Black Southerners. When your people and community have been culturally, socially, and politically oppressed, a few boos don’t feel like much. This resistance was evident in André 3000’s impassioned delivery of an acceptance speech, that served not only as a rebuke of bicoastal elites but a reverent call to arms for every rapper in the Southern United States.
"It’s like this though. I’m tired of folks. You know what I’m saying? Close minded folks. You know what I’m saying? It’s like we got a demo tape and nobody wants to hear it. But it’s like this. The South got something to say. That’s all I got to say."
Those words, uttered by a young André 3000, echoed through the South. Although the Atlanta group was the first Southern group to achieve mainstream recognition for their work, the first Southern hip-hop group to reach commercial success was the Geto Boys from Houston. Texas — a state, which is often referred to as its country, an amalgamation of different regional dialects and sounds — laid the foundation for André’s charge.
After the duo left The Source Awards stage, they swore to Goodie Mob, another Atlanta based group in attendance, "One day they’re gonna have to f— with us." Months after the 1995 Source Awards, Goodie Mob released their own critically acclaimed debut, Soul Food. The album propelled Southern hip-hop to the masses, and featured a track entitled "Dirty South." The term, first used by Atlanta rapper Cool Breeze, gave a name to the burgeoning hip-hop movement south of the Mason-Dixon line.
Instead of rejecting the coastal elitism of hip-hop, the Dirty South embraced it — in fact they sold it. Rappers from the Dirty South did not emulate New York or L.A style; they reinterpreted and investigated cultural perceptions and stereotypes about being country, backwards, forgotten to the time and the nation. Southern rappers also interrogated America’s past, present and future. For Black Southerners — whose cultural hallmarks and cornerstones are distinctly entwined with remnants of the Confederacy, the Klan, and the Civil Rights movement — hip-hop gave the ability to document a region and people lost to the American consciousness.
The aesthetics of Southern hip-hop were rooted in the power and reclamation of things once thought to be country: Gold dental crowns evolved into grills; the four pack of oversized white tees from the dollar store became a nightlife staple; André 3000, Pastor Troy, Lil Jon and Ludacris reinterpreted the Confederate flag. The attire of strippers from across the South became the blueprint for women’s fashion. Cash Money introduced "Bling Bling" into the American consciousness.
While East Coast rap was heavily influenced by musical stylings of immigrants from the Caribbean with notes of funk and soul, rap in the Dirty South took inspiration from blues and gospel — genres birthed from hymns and psalms sung in the fields and plantations. The Dirty South brought their ancestors with them. Their rap style and delivery had an inherent country twang, an accent reminiscent of a period lost to time yet modern; its incorporation of rock 'n' roll, jazz, and funk embodied a contemporary Southern spirit.
If the introduction of West Coast rap struck fear in the East Coast, the South was a laughing stock, until the South started to sell in the early to mid 2000s. Some critics attribute the ascension of Southern hip-hop to the fatigue of the East vs. West Coast rivalry. Others say hip-hop was in need of a new start after the early passings of the Notorious B.I.G. and Tupac Shakur. Whether both claims are true or false, the Dirty South was the future.
Notable Southern Hip-Hop Artists & Labels
Atlanta: The epicenter of the Dirty South. In the early 1980s, Atlanta' hip-hop started to get its foothold with airplay on local radio stations, artists being signed to Miami-based record labels, and early success on the music charts and the GRAMMYs. Rapper Mo-Jo, club DJ King Edward J, and Peter "MC Shy D" Jones were among the first in the city’s hip-hop community. At the time Jones was signed to Luke Records, a Miami based record label started by Luke Campbell of the 2 Live Crew. The hyper localized scene benefited from the contributions of club DJs Kizzy Rock and DJ Smurf, who shifted Atlanta’s sound from a Miami bass derivative into a distinctive sound.
From the mid 1980s, a number of local record labels emerged: Ichiban Records and Wrap Records. However when Antonio "L.A." Reid and Kenneth "Babyface" Edmonds moved to Atlanta in 1989, the local hip-hop scene changed. In the 1990s, their LaFace Records signed Goodie Mob, Outkast, producers Organized Noize, TLC, Usher, Xscape and others. Meanwhile, Jermaine Dupri founded So So Def record label. Under the direction of Lil Jon, the label’s A&R, the label signed Xscape, Da Brat, Jagged Edge, and more acts aligned with the R&B/hip-hop sound. As the signees of LaFace and So So Def Records triumphed, Def Jam Records hired Scarface of the Geto Boys to lead their Southern division, Def Jam South, which signed Ludacris.
As a solo artist Lil Jon & The East Side Boyz released "We Still Crunk Up!,""Put Yo Hood Up,""Kings of Crunk," and "Crunk Juice," a series of albums credited with bringing crunk into the mainstream. The popularity of crunk and dance music was heralded by Crime Mob, D4L, Dem Franchise Boyz, Soulja Boy and more who gave Atlanta hip-hop prominence not only in music but Internet culture.
New Orleans: In the aftermath of bounce music’s expansion in the early 1990s, Parkway Pumpkin’ Records was the holding place of New Orleans’ talent. Mystikal, known then as Mystikal Mike, was one of the label’s early signees. Along with Magnolia Slim, an architect of the New Orleans hip-hop sound. At the time, Parkway Pumpkin were free to record with other labels like Big Boy Records. When Master P moved back home from the Bay Area, his No Limit Records existed alongside local independent record labels like Cash Money, Take Fo’, Tombstone and Untouchable.
In a strategic business move, No Limit Records took Mystikal, Soulja Slim (formerly known as Magnolia Slim), and producer KLC from Parkway Pumpkin. As well as the signing of his family members C-Murder, Silkk the Shocker, Master P signed Mia X, the first lady of No Limit Records to the label. KLC, known as Craig S. Lawson, formed Beats by the Pound, the production behind No Limit Records. One of his first productions, Down South Hustlers, a compilation tape that featured New Orleans' first rap group New York Incorporated, signified No Limit Records attempt to exemplify Dirty South culture. Although No Limit Records secured a major label investment in 1996, Cash Money Records emerged in 1998 as a challenger with their new signees of Juvenile, Big Tymers, Hot Boys, and Lil Wayne with production by Mannie Fresh.
Memphis: At Club No Name, the first club in Memphis to play hip-hop, DJ Spanish Fly originated as one of the first creators to bring Memphis rap into shape. Although the patrons’ preference skewed towards electro, DJ Fly would incorporate his own preferences into mixes at Club No Name, Club Expo, and the Crystal Palace Skating Rink. His mixes maintained an ominous groove that included notes of electro but made room for moody rap. Though DJ Spanish Fly was among the first to evolve Memphis rap, DJ Squeeky defined the city’s sound with the insertion of a SP-1200 and Roland keyboard.
His influence can be heard in early mixtapes from DJ Paul and Juicy J. DJ Paul and Lord Infamous, his half brother formed the Serial Killaz. When the duo met with Juicy J, the three formed The Backyard Posse. Over time, the group added Koopsta Knicca, Crunchy Black, and Gangsta Boo. The six person group was renamed Three 6 Mafia and released their first album, Mystic Stylez under Prophet Records. Mystic Stylez also featured the female rapper La Chat and Project Pat, the brother of Juicy J. Shortly after their deal, the group parted ways with Prophet and formed their own label Hypnotize Minds. La Chat also released "Murder She Spoke," her debut album on the record label.
Under the direction of DJ Paul and Juicy J, the rappers under the Hypnotize Minds label achieved commercial and critical success, as well as an Academy Award for It's Hard Out Here for a Pimp" for Hustle & Flow, a drama set in Memphis that follows DJay (played by Terrence Howard), a pimp and drug dealer with aspirations of becoming a rapper.
Miami: Before hip-hop migrated down from New York, Miami already had a DJ style. In Miami, the DJs would be "regulating": or "mic checkin','' where the DJ brought down the record for a short period of time and insert their own lyrics to remix the song in a similar fashion to reggae and dancehall DJs. In the late 1970s and early 1980s, DJs would travel with their generators, turntables, speakers, and equipment to perform in public and private spaces across the city.
As local DJs put their spin on hip-hop, the city’s rappers energetic sound which came to be known as Miami bass, a diasporic influenced heavy bass sound that contained elements of electro and synthesizers were heard in the music of the Gucci Crew, Clay D, MC A.D.E., and the 2 Live Crew. The 2 Live Crewwas the first to bring the Miami bass sound to the mainstream. The group released their albums under then Skyywalker Records (now Luke Records), member Luther Campbell’s record label. Their success came at a cost. The sexually explicit nature of their lyrics resulted in a federal court obscenity trial, which established the precedent for censorship in music.
In the mid to late 1990s, Slip-n-Slide Records, a label founded by Ted Lucas, signed Trick Daddy, a Liberty City resident who thematically used the language of gangsta rap to speak about the struggles and challenges of living in a disenfranchised area. However, it was Trina who joined Trick Daddy on "Nann N—a," who put the city, its women, and women across the Dirty South with her as refuted Trick Daddy on his own track. "Da Baddest Bitch," her debut album released on Slip N Slide label put her in conversation with Lil' Kim and Foxy Brown as a contender for the Queen of hip-hop title.
Subgenres Of Southern Hip-Hop
For the past two decades, the Dirty South has been responsible for hip-hop’s expansion and evolution. The region has conducted a variety of sonic experiments and melodic sounds to produce an expansive lexicon that represents the conflict, tension, and joy about being Black in the South.
Southern hip-hop does not shy away from the underground, but rather embraces it. The music in itself is a contradiction: A track used for shaking ass at the strip clubs, while patrons eat chicken wings, can originate from a gospel beat. Because to be Black in the South, where your ancestors were once enslaved, is disorienting.
Bounce music: New Orleans has a vast musical history and structure: The chanting of the Mardi Gras Indians, the brass of the second line bands, and the expressiveness of parade culture cultivated a music of lively and celebration. When hip-hop arrived, it incorporated notes of the existing styles into a call-and-response formula over a series of rhythmic beats which invoked attendees into dance. Originating in the city's housing projects, this new style of bounce music took a new life in the city’s nightlife. Folks felt called to participate in the chanting, the hyper-localized lyrics, and high energy drum patterns familiar to second line culture. Although Big Freedia, is known as the Queen of Bounce Music, and rightfully so. The musician got their start working with Katey Red, "the first trans woman bounce artist."
Buck music: Within Memphis’ skating rinks and club cultures a dance music that ricocheted through the body, was born. Local DJs reinterpreted samples of soul and funk music, keyboard melodies of the Black church, with distinctive time signatures and cadences, on top of electronic-focused bass to give rise to a lexicon of dance styles including jookin’ and stomping. The heavy bass music stylings of Memphis also gave birth to trap and crunk, two styles most associated with Atlanta.
Crunk music: What would crunk music be without its patron saint Lil Jon? Although the rapper-producer cannot lay claim to the origins of the musical style, in the early 2000s, Lil Jon & the Eastside Boyz brought crunk to popular culture. Known for its party-centered lyrics and uptempo rhythms, crunk music became synonymous with Atlanta’s club and strip culture. The shouting, the energetic call and response, the chanting; crunk became the loud, bold, vocal expression of the city’s youth and music culture. To be crunk was to be excited.
Snap music: Snap music, an Atlanta-based form of hip-hop, was ushered in by the rise of handheld technology and social media sites like YouTube in the early 2000s. In lieu of a snare or clap, a snap was inserted as a replacement, often complemented by a whistle. The songs, which shared components of crunk, were exemplified by an accompanying dance and uploaded to social media sites (in much the same way Gen Z does on TikTok).
Miami bass: Miami, the city of two Souths. One foot in the Southern United States, the other in the geographical South. The demographic, geographic, and cultural mix of Cuban and Haitian, as well as Southern Blackness, produced an eccentric style of hip-hop. Elongated bass built on layered rhythmic production, and short, repetitive phrases ushered in a shout and response style became hallmarks of Miami bass. Played around 125 beats per minute, the style flourished in Miami’s car scene as well as party and adult entertainment culture.
Trap music: If crunk and snap music were symbols of the jovial Atlanta, then trap emerged as a symbol of the city and Black America’s underground. In a nation where Black communities experienced the onslaught of War on Drugs policies and excessive policing, the only way towards economic freedom was to hustle, and the hymn of the hustle and struggle was trap. Embedded with the dark lyrical content, multilayered kick drums, hi hats and synthesized drums was the moodiness of the duffle bag boy trying to survive. Over time, a holy trinity of the Roland TR-808, snare rolls, and first hand experience gave birth to a style where dope boys could be referred to as kings.
Definitive Southern Hip-Hop Songs
Three 6 Mafia - "Tear Da Club Up '97" (1997): The conveying of electric bodies in movement can result in one of two ways. The first, a baby. The second, an ass whooping. The club is also a multifaceted place where you can meet the love of your life or the person (or people) who have been "talkin' that s—," as Three 6 Mafia say. This is the environment where "Tear Da Club Up" resides.
The song serves as a call to action. On a good night, the song is a declaration of celebration. On a bad night, an ominous premonition of what’s to come. "Tear Da Club Up" was banned in 17 states, but established the precedent for crunk anthems like "Knuck If You Buck," and the movement of club-esque songs that served a dual purpose for fighting.
"Tear Da Club Up" remains a reminder of what a night out looks like with Three 6 Mafia.
Gangsta Boo -"Where Dem Dollas At" (1998): In an industry, where the contributions of Black women are used to build the empires of men in hip-hop, Gangsta Boo refused to be silenced. She knew that the voices of young Black women and girls from the South, belonged at that table.
While Juicy J and DJ Paul used Three 6 Mafia to construct their own kingdom in the Third Coast, Gangsta Boo did not sit idly by. Her appearances on Three 6 Mafia's "Mystic Stylez" and "Enquiring Minds" were small glimpses of her power, but her christening was "Where Dem Dollas At." The Queen of Memphis had arrived.
Her presence made the appearance of Juicy J and DJ Paul irrelevant. Her lines became a chant, a psalm, a swift rebuke for every woman who had been taken advantage of by a man and needed a fierce reminder of their power. It made men in Memphis and hip-hop understand exactly what it meant to be a lady from the Third Coast: to endure, to preserve, and to hustle when the odds are against you. To this day if you hear a woman recite "Where Dem Dollas At," know she has conjured the spirit of Gangsta Boo and it would be best to return the money owed by you.
Trick Daddy feat. Trina - "Nann N—" (1998): Hip-hop has always encouraged the back and forth among emcees — the exchanging of verses, the pointed attention to detail, the eventual crescendo to eviscerate an opponent. There is a reason why battle rap is tethered to its name. Although the spirit of competition has always been omnipresent, the battles were always centered around men. Whenever a woman enters the battle and annihilates an opponent — as Roxanne Shanté did at the Battle for World Supremacy — the man still emerges as the victor. It was as if femininity was the deciding factor of who could win a battle or not. Until Trina came around.
That is not to say Trina was the first to win a one-on-one battle with a male MC. But, she is the first to utilize femininity in a pointed way to take down an opponent. The first half of "Nann N—" is an elongated list of the ways masculinity has empowered Trick Daddy. In the second half, Trina details the ways her femininity grants her access to things Trick Daddy could not even dream of. The deployment of her sly, viperous lines and sweet, Southern wit took apart Trick Daddy’s line bit by bit. Until she was left as the last person standing.
The positive reception and response to "Nann N—" placed Trina in conversation with the women rappers of that era, and laid the framework for the next generation of women rappers from the South.
Juvenile feat. Mannie Fresh & Lil Wayne - "Back That Azz Up" (1999): The opening notes of "Back That Azz Up" are all it takes for people to throw their booties in a series of fashions. Whether circular or up down, the song does not shake about the positionality of where you throw ass, as long as you are shaking it.
The holy trinity of Mannie Fresh, Juvenile and Lil Wayne not only introduced New Orleans bounce music into the mainstream, but jump started Cash Money Records' takeover of the 2000s. There is no greater party song, revered by people of all generations, genders, races, and creeds than "Back That Azz Up."
Crime Mob feat. Lil Scrappy - "Knuck If You Buck" (2004): For Black youth in the South, there are few outlets to express rage. Crunk music is emo music for Black people, and provides the language to release and move through the torments of being Black in America. For a group of teenagers from outside of Atlanta, Crime Mob were the originators of this type of youth-specific music.
The group, composed of M.I.G., Cyco Black, Princess, Lil' Jay, Diamond, and Killa C. were the voices of young Black Atlanta.
Recorded in a closet at producer Lil Jay’s house with a knockout track by his little sister, Princess, "Knuck If You Buck" became a rallying cry for Southern teens. With a beat inspired by a brawl at Lil Jay’s house and the stylings of DJ Paul and Juicy J, the song quickly became the group’s biggest hit.
"Yeah, we knuckin and buckin and ready to fight. I betcha I'ma throw them things, so haters best to think twice," became the go-to chant for a country-ass brawl. With the addition of Diamond’s delivery of "Bitch you irrelevant, step to my residence. Best to back up 'fore I fill you with lead," in the fourth line; the song solidified the pair (Diamond and Princess) as the breakout stars on the collective track.
Their presence welcomed women to the crunk fight. Where their verbal expressions of anger and violence were warmly received for over 15 years, generations of Black youth have sought solace in this song and whooped ass to it as well.
Southern Hip-Hop Artists On the Rise
If the Dirty South is the future, the future of Southern hip-hop is female. Jucee Froot, GloRilla, Doechii, Kaliii, KenTheMan, Monaleo, TiaCorine and Baby Tate are among the latest rappers to carry the Dirty South sound and aesthetic. Meanwhile, Saucy Santana and Lil Nas X are changing the South's presentation in terms of gender identity and expression.
Cultural and societal perceptions of the South have changed greatly, in due part to a new generation of entertainers who champion the South on a continual basis: Houston has found another champion in Megan Thee Stallion; Miami’s new voice is found in the City Girls; in Memphis, GloRilla is carrying on the legion of Gangsta Boo who died in January of this year; and Atlanta has a diverse array of women rappers that prove the city does not have one singular sound.
By the early 2000s, the classifier "Dirty South" became less of a communal touchstone and more of a marketing term by record labels in Atlanta. But it was less of a marked loss and more of a massive cultural shift.
By the mid 2000s, Southern rappers became the dominant voices in hip-hop, and largely took over pop culture. Evidenced by trap music migrating out of Atlanta to pop and genres across the world, the cultural exports of Southern hip-hop can also be found in streetwear and luxury fashion.Within the industry, Dirty South legends like Lil Wayne were honored at the Black Music Collective’s Recording Academy Honors during the 2023 GRAMMY Awards.
A Guide To Southern California Hip-Hop: Definitive Releases, Artists & Subgenres From L.A. & Beyond

Photo: Erika Goldring/Getty Images
list
6 Takeaways From Megan Thee Stallion's 'Megan': Snakes, Shots & Self-Assurance
From the serpentine theme to Japanese rhyme schemes, Megan Thee Stallion's third album snatches back her own narrative and isn't afraid to take a bite.
Beware of venom: Megan Thee Stallion is not biting her tongue on her new album, simply titled Megan.
The GRAMMY winner's first full-length release in two years is also the first to drop under her own control. Fans have been ready for this release even before the first single, "Cobra," came out in November. The second single, "Hiss," followed in January and brought the star her first No. 1 hit on the Billboard’s Hot 100 and Global 200 charts. These songs, as well as the third single, "BOA," foreshadowed a certain slithery theme that helped shape the album.
Megan was released on June 28 and features guest stars such as GloRilla, Victoria Monét, Big K.R.I.T. and Kyle Richh as well as her longtime ace producers like Juicy J (who made "Hot Girl Summer" among other calling cards) and LilJuMadeDaBeat, who produced Stallion anthems like "Big Ole Freak," "Body" and "Thot S—."
Here’s what we learned from listening and vibing to the latest work by three-time GRAMMY winner Megan Thee Stallion.
A Theme Snakes Through Megan
As could have easily been predicted from the first three singles "Cobra," "Hiss" and "BOA," and now the album track "Rattle," there is a hint of a snake theme that wends its way through the album from beginning ("Hiss") to end ("Cobra").
In several songs, she denounces all the snake behavior that she has encountered from former lovers, friends, and haters who support those who have caused actual harm to her. In the music video for "Cobra," Megan literally sheds her old skin to reveal a shining new layer.
Megan Is Calling The Shots This Time
"I feel like Biggie, 'Who Shot Ya?’/But everybody know who shot me, bitch/ So now, let’s stop speaking on the topic," she rapped in "Who Me (feat. Pooh Shiesty)" off her 2022 album Traumazine. MTS was referencing the July 2020 incident in which rapper Tory Lanez shot her in the foot, and was subsequently charged with assault with a semiautomatic firearm and carrying a loaded, unregistered firearm in a vehicle.
Turns out, she wasn’t done referencing the topic. Now, she’s one taking the shots. MTS takes aim at less-talented women rappers on "Figueroa" (named for a Los Angeles street known for prostitution), and at Lanez on "Rattle," when she suggests that his male supporters should schedule a conjugal visit with him in prison. (Lanez is currently serving a 10-year sentence while simultaneously going through a divorce with wife Raina Chassagne.)
More Megan Thee Stallion News & Videos

6 Takeaways From Megan Thee Stallion's 'Megan': Snakes, Shots & Self-Assurance

9 Epic Sets From Bonnaroo 2024: Ethel Cain, Melanie Martinez, Megan Thee Stallion & More

5 Iconic Moments From Megan Thee Stallion's Houston Hometown Shows

Everything We Know About Megan Thee Stallion's New Album 'Megan': Tracklist, Release Date & More

15 LGBTQIA+ Artists Performing At 2024 Summer Festivals
Inspiration Comes From Everywhere
The star and her collaborators incorporate unexpected musical influences on Megan via creative sampling. Megan Thee Stallion speeds up and flips Teena Marie's 1984 ballad "Out on a Limb" for "B.A.S." — a song she co-produced with her longtime ally LilJuMadeDaBeat. "BOA" is cleverly crafted from sounds in the first solo hit by Gwen Stefani, 2004’s "What You Waiting For?"
UGK are reunited from across the heavenly divide on the Juicy J-produced "Paper Together," with Bun B contributing new work and the late Pimp C joining in lyrical spirit. This is especially significant when considering that Juicy J produced "Intl’ Players Anthem (I Choose You)," UGK’s 2007 hit with Outkast. Juicy J also made the beats for Megan’s famous song "Hot Girl Summer."
That’s just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to samples waiting to be discovered on Megan. There are many more riffs and other musical notions that the sample bank in our brains have yet to detect.
Self-Love Is Queen
Whether she’s affirming, "I’m worthy, not worthless" on "Worthy," or literally touching herself in the auto-erotic "Down Stairs DJ" (which joins masturbation masterpieces like Divinyls’ "I Touch Myself" and Tweet’s "Oops"), Megan is grounded in songs that promote self-love as the best kind of love.
She does admit that this is sometimes a challenge to embody, as when she talks about lingering depression on "Moody Girl." But the album generally moves towards the light.
She Loves Japan
One of the big surprises on Megan is that she raps in two languages. She rhymes beautifully in Japanese on "Mamushi" with Yuki Chiba, a seasoned rapper from Japan who is influenced by the Southern swag. (Just take a look at the Memphis moves and Houston rhyme schemes of his viral song "Team Tomodachi.")
On "Otaku Hot Girl," she raps about the manga series "Naruto" and drops other anime references to show her love of Japanese pop culture.
Learn more: 10 Neo J-Pop Artists Breaking The Mold In 2024: Fujii Kaze, Kenshi Yonezu & Others
Megan's Game Is Tight
Megan is the first album to be released on Megan Thee Stallion’s own label. It follows her split from 1501 Certified Entertainment, a record label with which she was engaged in a protracted and ugly legal battle for earnings.
She now has the muscle of the major label Warner Brothers as a partner for her independent venture, Hot Girl Productions. She also recorded an Amazon Original song called "It’s Prime Day" for a commercial, as well as an exclusive Amazon edition of Megan.
It’s safe to say that this album represents a new level of business freedom and acumen for Megan Thee Stallion.
PRIDE & Black Music Month: Celebrating LGBTQIA+ & Black Voices

Celebrating 30 Years Of Essence Fest: How New Orleans & Multi-Generational, Diasporic Talent Create The "Super Bowl Of Culture"
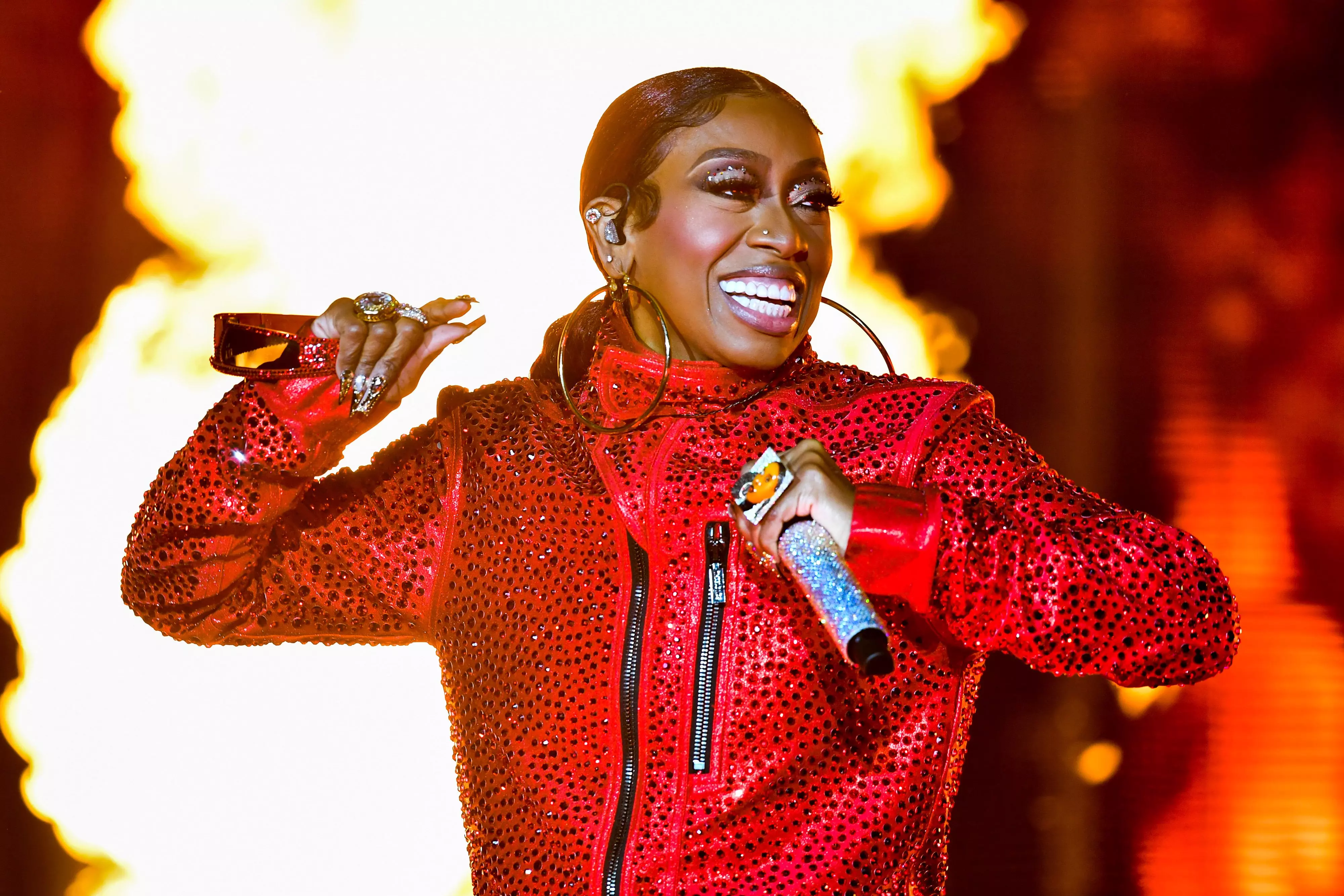

Celebrating Missy Elliott: How The Icon Changed The Sound, Look & Language Of Hip-Hop

Tekno Talks New Music, Touring America & His "Elden Ring" Obsession

5 LGBTQIA+ Record Labels To Check Out: Get Better Records, So Fierce! And Others
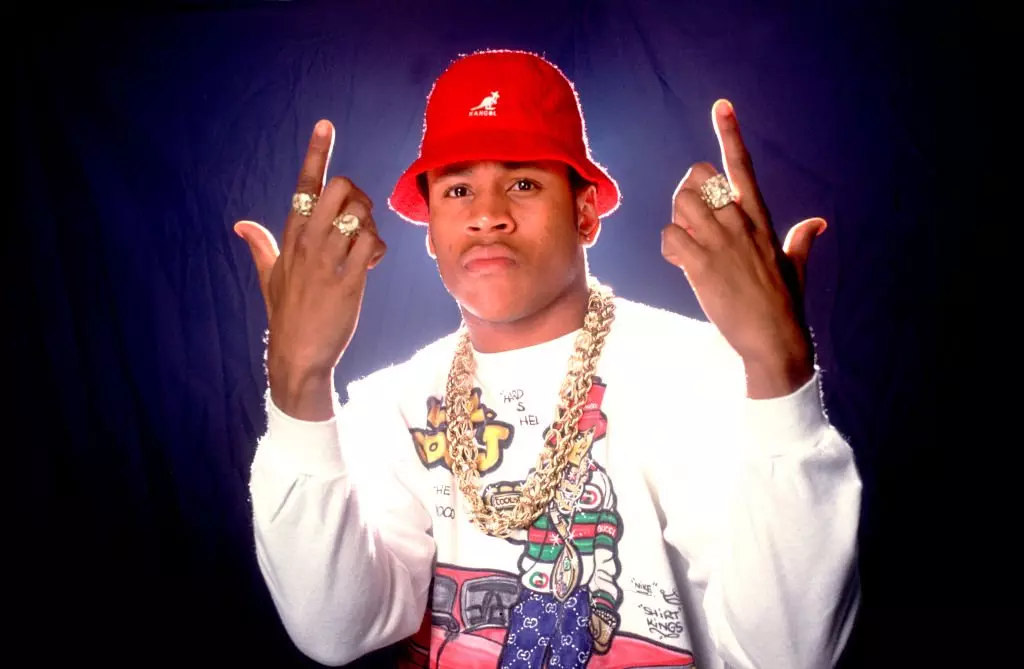

Celebrate 40 Years Of Def Jam With 15 Albums That Show Its Influence & Legacy

Photo: Julia Beverly/Getty Images
news
Remembering Producer Rico Wade, Helped Define The Sound Of Southern Hip-Hop
Rico Wade, legendary producer and one-third of Organized Noize, who helped forge the sound of Atlanta hip-hop and propelled artists like OutKast, Ludacris, and TLC to fame, has died at 52.
Hip-hop has lost another legend. Rico Wade, an integral part of the bedrock of Southern hip-hop, the godfather of modern Atlanta rap, and one-third of the production crew Organized Noize with Patrick "Sleepy" Brown and Ray Murray, has died. He was 52.
Wade was a force that helped launch the careers of OutKast, Goodie Mob, Ludacris, and Future, and produced and co-wrote hits for artists including TLC's "Waterfalls," as part of a mid-'90s Southern hip-hop renaissance. The epicenter of this revolution was the Dungeon, his mother's basement in East Point, Georgia. The location built a reputation as a haven for Dungeon Family artists like André "André 3000" Benjamin and Antwan "Big Boi" Patton among a generation of ATL creatives formulating their own flavor of Southern rap.
"We're deeply saddened by the passing of Rico Wade, one of Atlanta’s most prolific music producers," said Recording Academy CEO Harvey Mason jr. "Rico's influential contributions to the Atlanta music scene beginning in the 1990s helped foster the rise of some of hip-hop’s most prominent artists and played a pivotal role in shaping the genre as we know it today. Our hearts go out to his family, friends, and all those whose lives he influenced.”
Wade was nominated for two GRAMMYs during his lifetime including Record Of The Year for TLC's "Waterfalls" and Album Of The Year for OutKast's Stankonia.
“Rico left an indelible mark on music and culture around the world and for that, the South will always have something to say,” said Atlanta Mayor Andre Dickens in an issued statement echoing the famous battle cry of André 3000's 1995 Source Awards Best New Artist acceptance speech.
It's been more than 30 years since OutKast dropped their first-ever single "Player's Ball" in 1993 and on that track Wade's voice is the first. He sets the tone for the legendary duo's entire career and Southern hip-hop at the same time with the introduction: "Man, the scene was so thick/ Lowriders, '77 Sevilles, El Dogs/ Nothin' but them 'Lacs/ All the players, all the hustlers/ I'm talkin' 'bout a Black man heaven here/ You know what I'm sayin'?"
"Rico Wade brought us to his house studio, where I heard the most interesting music production I'd ever heard from Atlanta," André 3000 told the Recording Academy in a 2019 interview reflecting on his experience working on OutKast's debut album Southernplayalisticadillacmuzik. "It was Rico, Ray, and Sleepy's vision to make sure [OutKast would put] Southern lifestyle first. I was just playing my part the best I could."
Outkast's Southernplayalisticadillacmuzik would go on to sell 500,000 records and became certified platinum within a year. "When we were working on the OutKast vibe, even though there were two members in the group, we all considered ourselves OutKast at the time — including all of Organized Noize and the Goodie Mob members who appeared on the album," Murray told the Recording Academy in 2019.
Read more: OutKast Examine Their Southern Experience On 'Southernplayalisticadillacmuzik'
Organized Noize signed a publishing deal with L.A. Reid and Babyface's label LaFace Records in 1993, setting the foundation for their work on OutKast's seminal "Player's Ball" single. It was a lasting connection that would serve the rest of Wade's career.
Wade would continue to work with Reid during Reid's tenure as chairman and CEO of Epic Records from 2013 to 2017, building a hub for hip-hop artists at the label including Wade's cousin, Atlanta rapper Future. Future would become the first artist ever on the Billboard charts to debut back-to-back albums at No. 1 with his 2017 release HNDRXX. In March, Future and Metro Boomin jointly released another No.1 album, We Don’t Trust You.
Wade nurtured Future's talents through his Dungeon connects. The two didn't meet until Future was well into his teens, but once they did Wade quickly put his cousin's clear drive and talent to use, introducing him to the Dungeon Family and bringing him into the studio to work on in-house production projects including Ludacris' "Blueberry Yum Yum" (Red Light District), which earned Future a songwriting credit in 2004.
“That's how he ended up writing the record for Ludacris, becoming part of a group that could make music, and getting a record deal,” Wade told Complex in 2013. “It showed him that the music industry money is real."
Inspired by his cousin, Future studied the industry through the in-roads made by Wade. “I took everything I learned from him and applied it to my everyday craft from being in the studio,” Future told Complex. "Just knowing how to feel records so I know how to make songs and write for people to keep around and go to the next level.” His devotion to Wade's tutelage and legacy is apparent in the Olde English script tattooed across his arms that matches Wade's own markings — "DUNGEON" appears on the right and "FAMILY" on the left.
Killer Mike, a constant collaborator who worked with Wade on his latest album Michael which swept the 2024 GRAMMYs rap categories with three wins for Best Rap Album, Best Rap Song, and Best Rap Performance, announced Wade's passing in an Instagram post on Sunday. "I don't have the words to express my deep and profound sense of loss. I am Praying for your wife and Children. I am praying for the Wade family. I am praying for us all," Killer Mike wrote. "I deeply appreciate your acceptance into The Dungeon Family, mentorship, Friendship and Brotherhood. Idk where I would be without ya'll."

Photo: Michael Ochs Archives/Getty Images
feature
'Run-DMC' At 40: The Debut Album That Paved The Way For Hip-Hop's Future
Forty years ago, Run-DMC released their groundbreaking self-titled album, which would undeniably change the course of hip-hop. Here's how three guys from Queens, New York, defined what it meant to be "old school" with a record that remains influential.
"You don't know that people are going to 40 years later call you up and say, ‘Can you talk about this record from 40 years ago?’"
That was Cory Robbins, former president of Profile Records, reaction to speaking to Grammy.com about one of the first albums his then-fledgling label released. Run-DMC’s self-titled debut made its way into the world four decades ago this week on March 27, 1984 and established the group, in Robbins’ words, "the Beatles of hip-hop."
Rarely in music, or anything else, is there a clear demarcation between old and new. Styles change gradually, and artistic movements usually get contextualized, and often even named, after they’ve already passed from the scene. But Run-DMC the album, and the singles that led up to it, were a definitive breaking point. Rap before it instantly, and eternally, became “old school.” And three guys from Hollis, Queens — Joseph "Run" Simmons, Jason "Jam Master Jay" Mizell, Darryl "D.M.C." McDaniels — helped turn a burgeoning genre on its head.
What exactly was different about Run-DMC? Some of the answers can be glimpsed by a look at the record’s opening song. "Hard Times" is a cover of a Kurtis Blow track from his 1980 debut album. The connection makes sense. Kurtis and Run’s older brother Russell Simmons met in college, and Russell quickly became the rapper’s manager. That led to Run working as Kurtis’ DJ. Larry Smith, who produced Run-DMC, even played on Kurtis’ original version of the song.
But despite those tie-ins, the two takes on "Hard Times" are night and day. Kurtis Blow’s is exactly what rap music was in its earliest recorded form: a full band playing something familiar (in this case, a James Brown-esque groove, bridge and percussion breakdown inclusive.)
What Run-DMC does with it is entirely different. The song is stripped down to its bare essence. There’s a drum machine, a sole repeated keyboard stab, vocals, and… well, that’s about it. No solos, no guitar, no band at all. Run and DMC are trading off lines in an aggressive near-shout. It’s simple and ruthlessly effective, a throwback to the then-fading culture of live park jams. But it was so starkly different from other rap recordings of the time, which were pretty much all in the style of Blow’s record, that it felt new and vital.
"Production-wise, Sugar Hill [the record label that released many key early rap singles] built themselves on the model of Motown, which is to say, they had their own production studios and they had a house band and they recorded on the premises," explains Bill Adler, who handled PR for Run-DMC and other key rap acts at the time.
"They made magnificent records, but that’s not how rap was performed in parks," he continues. "It’s not how it was performed live by the kids who were actually making the music."
Run-DMC’s musical aesthetic was, in some ways, a lucky accident. Larry Smith, the musician who produced the album, had worked with a band previously. In fact, the reason two of the songs on the album bear the subtitle "Krush Groove" is because the drum patterns are taken from his band Orange Krush’s song “Action.”
Read more: Essential Hip-Hop Releases From The 1970s: Kurtis Blow, Grandmaster Flash, Sugarhill Gang & More
But by the time sessions for Run-DMC came around, the money had run out and, despite his desire to have the music done by a full band, Smith was forced to go without them and rely on a drum machine.
His artistic partner on the production side was Russell Simmons. Simmons, who has been accused over the past seven years of numerous instances of sexual assault dating back decades, was back in 1983-4 the person providing the creative vision to match Smith’s musical knowledge.
Orange Krush’s drummer Trevor Gale remembered the dynamic like this (as quoted in Geoff Edgers’ Walk This Way: Run-DMC, Aerosmith, and the Song that Changed American Music Forever): “Larry was the guy who said, 'Play four bars, stop on the fifth bar, come back in on the fourth beat of the fifth bar.' Russell was the guy that was there that said, ‘I don’t like how that feels. Make it sound like mashed potato with gravy on it.’”
Explore The Artists Who Changed Hip-Hop
50 Artists Who Changed Rap: Jay-Z, The Notorious B.I.G., Dr. Dre, Nicki Minaj, Kendrick Lamar, Eminem & More
Hip-Hop Just Rang In 50 Years As A Genre. What Will Its Next 50 Years Look Like?

Watch Outkast Humbly Win Album Of The Year For 'Speakerboxxx/The Love Below' In 2004 | GRAMMY Rewind
A Brief History Of Hip-Hop At 50: Rap's Evolution From A Bronx Party To The GRAMMY Stage
GRAMMY Museum To Celebrate 50 Years Of Hip-Hop With 'Hip-Hop America: The Mixtape Exhibit' Opening Oct. 7

Watch Eminem Show Love to Detroit And Rihanna During Best Rap Album Win In 2011 | GRAMMY Rewind
Listen To GRAMMY.com's 50th Anniversary Of Hip-Hop Playlist: 50 Songs That Show The Genre's Evolution
14 New Female Hip-Hop Artists To Know In 2023: Lil Simz, Ice Spice, Babyxsosa & More
6 Artists Expanding The Boundaries Of Hip-Hop In 2023: Lil Yachty, McKinley Dixon, Princess Nokia & More
Watch 41 Bring The Hype With A Cover Of DMX's Hit "Party Up (Up In Here)" | Hip-Hop Re:Defined
The 10 Most Controversial Samples In Hip-Hop History

Watch Lauryn Hill Win Best New Artist At The 1999 GRAMMYs | GRAMMY Rewind
19 Concerts And Events Celebrating The 50th Anniversary Of Hip-Hop
Founding Father DJ Kool Herc & First Lady Cindy Campbell Celebrate Hip-Hop’s 50th Anniversary
A Guide To New York Hip-Hop: Unpacking The Sound Of Rap's Birthplace From The Bronx To Staten Island
A Guide To Southern California Hip-Hop: Definitive Releases, Artists & Subgenres From L.A. & Beyond
10 Crucial Hip-Hop Albums Turning 30 In 2023: 'Enter The Wu-Tang,' 'DoggyStyle,' 'Buhloone Mindstate' & More
The Nicki Minaj Essentials: 15 Singles To Showcase Her Rap And Pop Versatility
11 Hip-Hop Subgenres To Know: From Jersey Club To G-Funk And Drill
5 Essential Hip-Hop Releases From The 2020s: Drake, Lil Baby, Ice Spice, 21 Savage & More
A Guide To Southern Hip-Hop: Definitive Releases, Artists & Subgenres From The Dirty South
A Guide To Bay Area Hip-Hop: Definitive Releases, Artists & Subgenres From Northern California
A Guide To Texas Hip-Hop: Definitive Releases, Artists & Events

Ludacris Dedicates 2007 Best Rap Album GRAMMY To His Dad | GRAMMY Rewind
Unearthing 'Diamonds': Lil Peep Collaborator ILoveMakonnen Shares The Story Behind Their Long-Awaited Album
10 Bingeworthy Hip-Hop Podcasts: From "Caresha Please" To "Trapital"
Revisiting 'The Miseducation Of Lauryn Hill': Why The Multiple GRAMMY-Winning Record Is Still Everything 25 Years Later
Watch Asha Imuno Personalize Kendrick Lamar's "i" With A Sparkling New Chorus | Hip-Hop Re:Defined
10 Must-See Exhibitions And Activations Celebrating The 50th Anniversary Of Hip-Hop
5 Artists Showing The Future Of AAPI Representation In Rap: Audrey Nuna, TiaCorine & More
'Invasion of Privacy' Turns 5: How Cardi B's Bold Debut Album Redefined Millennial Hip-Hop
10 Songs That Show Doja Cat’s Rap Skills: From "Vegas" To "Tia Tamara" & "Rules"
Watch Olen Put A Dreamy, Melodic Spin On Childish Gambino's "Heartbeat" | Hip-Hop Re:Defined
6 Must-Watch Hip-Hop Documentaries: 'Hip-Hop x Siempre,' 'My Mic Sounds Nice' & More...
Essential Hip-Hop Releases From The 2010s: Ye, Cardi B, Kendrick Lamar & More
6 Takeaways From Netflix's "Ladies First: A Story Of Women In Hip-Hop"
How Drake & 21 Savage Became Rap's In-Demand Duo: A Timeline Of Their Friendship, Collabs, Lawsuits And More
5 Takeaways From Travis Scott's New Album 'UTOPIA'
Essential Hip-Hop Releases From The 2000s: T.I., Lil Wayne, Kid Cudi & More
Songbook: How Jay-Z Created The 'Blueprint' For Rap's Greatest Of All Time
Ladies First: 10 Essential Albums By Female Rappers

How Megan Thee Stallion Turned Viral Fame Into A GRAMMY-Winning Rap Career | Black Sounds Beautiful
How Hip-Hop Took Over The 2023 GRAMMYs, From The Golden Anniversary To 'God Did'
5 Things We Learned At "An Evening With Chuck D" At The GRAMMY Museum
Remembering De La Soul’s David Jolicoeur, a.k.a. Dave and Trugoy the Dove: 5 Essential Tracks
Catching Up With Hank Shocklee: From Architecting The Sound Of Public Enemy To Pop Hits & The Silver Screen
Meet The First-Time GRAMMY Nominee: GloRilla On Bonding with Cardi B, How Faith And Manifestation Helped Her Achieve Success
Hip-Hop's Secret Weapon: Producer Boi-1da On Working With Kendrick, Staying Humble And Doing The Unorthodox
Essential Hip-Hop Releases From The 1990s: Snoop Dogg, Digable Planets, Jay-Z & More
10 Albums That Showcase The Deep Connection Between Hip-Hop And Jazz: De La Soul, A Tribe Called Quest, Kendrick Lamar & More
Hip-Hop Education: How 50 Years Of Music & Culture Impact Curricula Worldwide
Women In Hip-Hop: 7 Trailblazers Whose Behind-The-Scenes Efforts Define The Culture

Watch Flavor Flav Crash Young MC's Speech After "Bust A Move" Wins In 1990 | GRAMMY Rewind
Essential Hip-Hop Releases From The 1980s: Slick Rick, RUN-D.M.C., De La Soul & More
Lighters Up! 10 Essential Reggae Hip-Hop Fusions

How Lil Nas X Turned The Industry On Its Head With "Old Town Road" & Beyond | Black Sounds Beautiful
9 Teen Girls Who Built Hip-Hop: Roxanne Shante, J.J. Fadd, Angie Martinez & More
Essential Hip-Hop Releases From The 1970s: Kurtis Blow, Grandmaster Flash, Sugarhill Gang & More
Killer Mike Says His New Album, 'Michael,' Is "Like A Prodigal Son Coming Home"
5 Takeaways From 'TLC Forever': Left-Eye's Misunderstood Reputation, Chilli's Motherhood Revelation, T-Boz's Health Struggles & More
Watch Eva B Perform "Sunrise In Lyari" Through The Streets Of Pakistan | Global Spin
It wasn’t just the music that set Run-DMC apart from its predecessors. Their look was also starkly different, and that influenced everything about the group, including the way their audience viewed them.
Most of the first generation of recorded rappers were, Bill Adler remembers, influenced visually by either Michael Jackson or George Clinton and Parliament-Funkadelic. Run-DMC was different.
"Their fashion sense was very street oriented," Adler explains. "And that was something that emanated from Jam Master Jay. Jason just always had a ton of style. He got a lot of his sartorial style from his older brother, Marvin Thompson. Jay looked up to his older brother and kind of dressed the way that Marvin did, including the Stetson hat.
"When Run and D told Russ, Jason is going to be our deejay, Russell got one look at Jay and said, ‘Okay, from now on, you guys are going to dress like him.’"
Run, DMC, and Jay looked like their audience. That not only set them apart from the costumed likes of Grandmaster Flash and the Furious Five, it also cemented the group’s relationship with their listeners.
"When you saw Run-DMC, you didn’t see celebrity. You saw yourself," DMC said in the group’s recent docuseries.
Read more: 20 Iconic Hip-Hop Style Moments: From Run-D.M.C. To Runways
Another thing that set Run-DMC (the album) and Run-DMC (the group) apart from what came before was the fact that they released a cohesive rap album. Nine songs that all belonged together, not just a collection of already-released singles and some novelties. Rappers had released albums prior to Run-DMC, but that’s exactly what they were: hits and some other stuff — sung love ballads or rock and roll covers, or other experiments rightfully near-forgotten.
"There were a few [rap] albums [at the time], but they were pretty crappy. They were usually just a bunch of singles thrown together," Cory Robbins recalls.
Not this album. It set a template that lasted for years: Some social commentary, some bragging, a song or two to show off the DJ. A balance of records aimed at the radio and at the hard-core fans. You can still see traces of Run-DMC in pretty much every rap album released today.
Listeners and critics reacted. The album got a four-star review in Rolling Stone with “the music…that backs these tracks is surprisingly varied, for all its bare bones” and an A minus from Robert Christgau who claimed “It's easily the canniest and most formally sustained rap album ever.” Just nine months after its release, Run-DMC was certified gold, the first rap LP ever to earn that honor. "Rock Box" also single-handedly invented rap-rock, thanks to Eddie Martinez’s loud guitars.
There is another major way in which the record was revolutionary. The video for "Rock Box" was the first rap video to ever get into regular rotation on MTV and, the first true rap video ever played on the channel at all, period. Run-DMC’s rise to MTV fame represented a significant moment in breaking racial barriers in mainstream music broadcasting.
"There’s no overstating the importance of that video," Adler tells me. vIt broke through the color line at MTV and opened the door to a cataclysmic change."
"Everybody watched MTV forty years ago," Robbins agrees. "It was a phenomenal thing nationwide. Even if we got three or four plays a week of ‘Rock Box’ on MTV, that did move the needle."
All of this: the new musical style, the relatable image, the MTV pathbreaking, and the attendant critical love and huge sales (well over 10 times what their label head was expecting when he commissioned the album from a reluctant Russell Simmons — "I hoping it would sell thirty or forty thousand," Robbins says now): all of it contributed to making Run-DMC what it is: a game-changer.
"It was the first serious rap album," Robbins tells me. And while you could well accuse him of bias — the group making an album at all was his idea in the first place — he’s absolutely right.
Run-DMC changed everything. It split the rap world into old school and new school, and things would never be the same.
Perhaps the record’s only flaw is one that wouldn’t be discovered for years. As we’re about to get off the phone, Robbins tells me about a mistake on the cover, one he didn’t notice until the record was printed and it was too late.
There was something (Robbins doesn’t quite recall what) between Run and DMC in the cover photo. The art director didn’t like it and proceeded to airbrush it out. But he missed something. On the vinyl, if you look between the letters "M" and "C,", you can see DMC’s disembodied left hand, floating ghost-like in mid-air. While it was an oversight, it’s hard not to see this as a sign, a sort of premonition that the album itself would hang over all of hip-hop, with an influence that might be hard to see at first, but that never goes away.
A Guide To New York Hip-Hop: Unpacking The Sound Of Rap's Birthplace From The Bronx To Staten Island
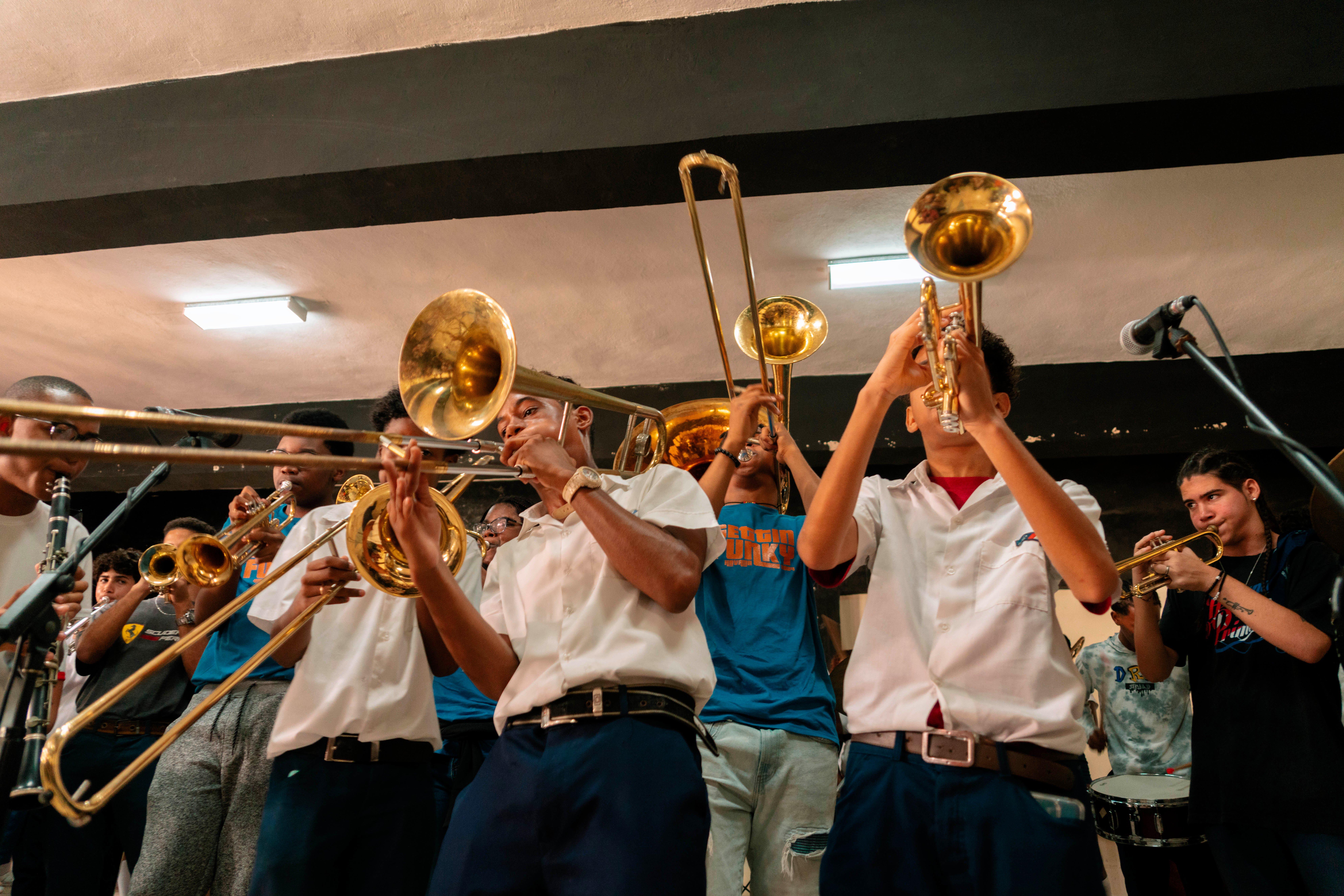
Photo: Eduardo Reyes Aranzaez
feature
At Getting Funky In Havana, Young Musicians Feel The Power Of Cross-Cultural Connection
An annual program organized by the Trombone Shorty Foundation and Cimafunk, Getting Funky In Havana explores the deep connections between Cuba and New Orleans — and provides student musicians with once-in-a-life-time learning opportunities.
It’s sweltering inside the Guillermo Tomas Music Conservatory, a primary school in Havana’s Guanabacoa neighborhood, where American visitors enjoy what will likely be the best school recital they'll ever see.
A series of teen and tween musicians — some in trios and quartets, others in larger ensembles — are playing a mix of Latin jazz, orchestral overtures and even a rousing rendition of the Ghostbusters theme. During an interpolation of Aretha Franklin's "Think," three young horn players burst to the front of the group in a competitive but friendly battle of brass.
The performance is the centerpiece of Getting Funky in Havana, a four-day music and cultural exchange program developed by GRAMMY-nominated Cuban funk artist Cimafunk, GRAMMY-winning New Orleans multi-instrumentalist Trombone Shorty's namesake foundation, and Cuba Educational Travel. Now in its third year, Getting Funky brought nearly 200 American music lovers, artists and students to Havana in January to explore the deep connections between Cuban and New Orlenian sounds through a series of performances, educational activities and panels.
"Cuba and New Orleans have a long line of influence, and we have special things that happen in both places that people can hear through our music," Trombone Shorty, born Troy Andrews, tells GRAMMY.com. "Passing along music and knowledge is…how the music's staying alive. I always try to tell the kids, learn everything that came before you, but also be very innovative."
While there are many conservatories in Havana, Guillermo Tomas was chosen in part for its similarities to New Orleans' Treme neighborhood, where many of the Trombone Shorty Foundation students live. Guanabacoa is "probably the deepest Afro-Cuban cultural neighborhood" in Havana, says Foundation Executive Director Bill Taylor.
Those shared roots and experiences were on display during several capstone concerts, which were also open to Havana residents. At a massive outdoor concert blocks away from Havana's famous Malecón, Getting Funky attendees enjoyed performances from Cuban salsa legends Los Van Van, reparto star Wampi and Shorty's Orleans Avenue. At a pinnacle performance the day before, more than 30 artists gathered at Havana arts hub La Fabrica for a sold-out international jam. Shorty, Big Freedia, Ivan Neville, percussionist Pedrito Martinez, PJ Morton, Tarriona "Tank" Ball, drummer Yissy Garcia and others joined forces with Cuban artists Reina y Real and X Alfonzo to create an unceasing groove.
Cuban and American students perform outside Guillermo Tomas┃Eduardo Reyes Aranzaez
While the concerts certainly brought the energy to a fever pitch, the beating heart of Getting Funky is its mission of music education. Ten members of the Trombone Shorty Foundation's brass band traveled to Cuba, where they performed at Getting Funky's opening night party and several other events. Throughout the week, the New Orleans students shared stages with their Cuban counterparts, learning each others' musical idioms and finding common ground.
"So much of the music [we hear in New Orleans comes] from Africa through the Caribbean to New Orleans, then spreading throughout the United States. When our students connect with those [Cuban] students, there's a natural, symbiotic connection that takes place," Taylor says.
High school senior and sax player Dylan Racine called the trip — his first time out of the country — a life-changing experience. "I learned so many new skills on this trip, including how to network, how to collaborate with young people from a different culture than me, and more," he says via email. Drummer and pianist John Rhodes, another senior, added that the experience was invaluable.
"I was able to interact with another culture and understand other young people through music. Although we couldn't speak the same language, we understood each other musically," he writes.
Both Cuba and New Orleans' unique musical cultures require constant innovation to survive, Taylor adds. "You honor the past, but it needs an infusion of new life in order to thrive. Getting Cuban musicians together with New Orleans musicians infuses a shot of energy into both of those musical styles."
The trip also put students from both countries in contact with working musicians, whose own perspectives were expanded by the experience.
"Music education and pedagogical expertise is so important. We need the next level to come up and be dope, just like we are," says trumpeter Keyon Harrold, whose work has taken him from sessions with Beyoncé to the 2024 GRAMMYs. This was Harrold’s second year at Getting Funky. "It's even more visceral and engaging to actually see these kids at the age of 10, 11, 12, and to know that in five years they're going to be the next."
For many of the musicians who attended, Getting Funky was an inspirational experience that furthered their existing work as well. "I perform for a living, but performing and playing with [students] is super dope. [Their energy is] clean," says GRAMMY-winning producer, rapper and mentor Deezle. "If I can in any way help to guide their path away from the pitfalls that I've encountered and endured, I would love to do that."
Legendary singer/songwriter Ivan Neville said he was blown away while watching young musicians from different worlds performing together. "This music was making their souls feel so good. I know music is good for the soul, but it was another level that I saw."
Fabio Daniel (center) and members of Primera Linea, or "first line"┃Eduardo Reyes Aranzaez
Since Getting Funky In Havana was established in 2020, the program has had a measurable impact on Cuban students' lives. In 2023, several young Cuban musicians traveled to New Orleans during JazzFest, where they visited Shorty’s studio and performed together at legendary venue Tipitina's. When the group returned home, they formed their own brass band, Primera Linea.
"This band is working; they are playing many places in Havana and that's thanks to the project. They were so into the satisfaction of [feeling] that they are valued," says Erik Alejandro Iglesias Rodríguez, who records as Cimafunk. "They are learning good quality things in terms of human relationships and in terms of music. [The program is] something that changes their mentality and lets them know that they can make it."
While Cuba harbors an incredible amount of musical talent, "making it" as a musician in the country comes with a unique set of challenges. The country's shrinking economy, high rate of inflation and low monthly incomes have 62 percent of Cubans reporting that they "struggle to survive" financially, according to a 2023 survey. Purchasing a professional calibur instrument, which may cost hundreds or thousands of U.S. dollars, often comes with great sacrifice.
It's an emotional day back at the Guillermo Tomas, where 10 of the school's top students will be awarded an instrument.
"An instrument is not something you can buy in a store," says Amanda Colina González, an art historian and one of the trip guides, who studied saxophone in conservatory. Colina González, like the majority of students, was given an instrument to play for the duration of her studies but had to return it to her school upon graduation. Remembering that moment brought tears to her eyes.
Because of its high cost and the possibility of leading to international travel, owning their own instrument can truly change a young musician's life. Getting Funky has donated approximately 50 instruments to Cuban students over three years of programming.
Fifteen-year-old Daniela Hernandez was awarded a trombone for her skill and dedication to music outside of school. Harried and teary-eyed after the recital, she shared her happiness and pride for being able to play with musicians who she's long admired. She plans to use her new trombone to study and will "take it with me everywhere."
Daniela and classmate Fabio Daniel (who received a trumpet during the first edition of Getting Funky in Havana in 2020) joined Trombone Shorty onstage at Getting Funky, performing for more than 15,000 people. Several of their friends and classmates brought their instruments to the concert — the largest held in Cuba in the last four years — and played back at the band from the crowd.
"Cuban musicians really enjoy playing and making other people feel joy through music,” Daniela says. Fellow trombone player and awardee Cristian Onel León says it's important to play for people outside of Cuba, and enjoys teaching people about his country's rhythms and keys. "I’m [also] learning other forms of playing, that aren’t mine. And it feels good,” he adds.
The program's instrument donation is spearheaded by the long-running nonprofit Horns To Havana, and supported by the Gia Maione Prima Foundation and private donors. Tickets purchased to attend the program also fund its efforts; Taylor says 2024's Getting Funky raised approximately $50,000. The Trombone Shorty Foundation hopes to continue the annual event, and expand into different countries; a 2025 Havana trip is already in the works.
For Rodríguez, who recently moved to New Orleans, the effect of this musical exchange is tangible. He's noticed more musicians who are open to collaborating across borders, and is working on new music with artists who have attended Getting Funky in previous years.
"Just jamming changes everything," he says. "That changes the minds of people; that changes the sound."
The connections made during Getting Funky have led to a variety of opportunities for students on both sides of the Gulf of Mexico. Foundation alto saxophonist Jacob Jones credits the trip for broadening his way of thinking while playing music; Deezle says he wants to get Cuban trumpeter and bandleader Fabio Daniel on a track; Primera Linea may perform at San Francisco's Outside Lands festival in August.
"To be able to facilitate that, and give to these young musicians of Cuba, is unbelievable," Andrews says of the program. "It's just a blessing to be able to be a blessing and help out the next generation, and help those musicians see a brighter future."
